Learn the importance and structure and whats is domain name. Discover how they differ from URLs and gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Understanding whats is domain name
- Structure of Domain Names
- Difference Between Domain Name and URL
- Registering whats is domain name?
- Managing Domain Name Security
- Importance of Choosing the Right Domain Name
- Transferring and Ownership of Domain Names
- Who Manages Domain Names?
- In Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding whats is domain name and its significance in the digital realm. The DNS protocol, is crucial for anyone navigating the online landscape. A domain name serves as an address that directs users to websites. It plays a pivotal role in establishing an online presence.
This blog post delves into the intricacies of domain names. By shedding light on their function, importance, DNS protocol, and how they impact businesses and individuals alike.
Understanding whats is domain name
Function of Domains

Domain names are crucial for identifying and tracking specific internet resources. They serve as the human-readable addresses that individuals use to access websites, send emails, or utilize any other online service. The significance of domain names lies in their ability to simplify internet navigation. By providing a recognizable and memorable naming system.
DNS resolution is the process through whats is domain name translated into their corresponding IP addresses. This translation enables computers to locate and connect with each other across the internet. By using these unique numerical identifiers and domain names. The DNS database plays a pivotal role in this process. By storing information about domain names and their associated IP addresses.
The DNS protocol operates through various domain name zones, each serving distinct purposes within the system. These zones include root zones, top-level domains (TLDs), second-level domains (SLDs), and subdomains. All contributing to efficient domain name management and resolution.
Whats is Domain Name Types
Top-level domains (TLDs) represent the highest level of domain names in the DNS hierarchy. They encompass generic TLDs like .com, .org, as well as country-code TLDs such as .uk and .ca for domain name. Second-level domains (SLDs) directly precede TLDs and cater to specific internet resources or general-purpose websites.
Subdomains are part of larger domain names; they can be used to create unique web addresses within a website’s main domain structure. Each type of domain name serves different needs based on its characteristics, making them essential components for establishing an online presence.
Structure of Domain Names
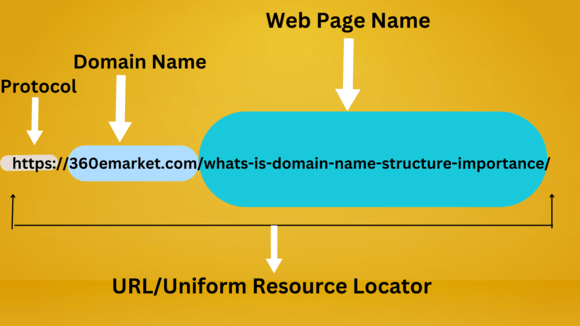
To understand whats is domain name composed of several essential components that form its hierarchical structure. The complete domain name consists of multiple levels separated by dots, with each level representing a specific part of the hierarchy. In “www.example.com,” “www” represents the host or subdomain, “example” signifies the second-level domain, and “.com” denotes the top-level domain.
Understanding the composition of whats is domain name involves recognizing these distinct elements and their respective positions within the overall structure. This includes comprehending the role of subdomains, second-level domains, and top-level domains in forming a cohesive and identifiable web address.
The essential components that make up whats is domain name play a crucial role in identifying and organizing internet resources within specific zones. By grasping these components and their arrangement within a domain name, individuals can effectively track and manage various online assets based on their categorization within this hierarchical system.
The format used for DNS messages and domain name is vital to facilitate effective communication between devices during DNS resolution processes. A typical DNS message format comprises various key sections such as header section, question section, answer section, authority section, and additional information section.
This structured format ensures that relevant information regarding domain names is accurately conveyed between different devices participating in DNS resolution activities. By understanding how DNS message formats and domain name are constructed and what each component signifies within these messages, users can gain insight into how data related to internet resources is managed across networks through the use of this critical protocol.
Difference Between Domain Name and URL
Definitions of Domain
They are the human-readable whats is domain name used to access websites. On the other hand, a URL is the specific address of a webpage within that website’s domain name. The DNS resolution process translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access internet resources seamlessly. This translation is made possible through the DNS protocol.
The DNS database plays a crucial role in storing whats is domain name and their corresponding IP addresses for efficient retrieval. It acts as a directory that keeps track of various domains and their associated IPs, ensuring smooth navigation across the web.
Understanding these key terms associated with domain name registration and management is essential for anyone looking to establish an online presence or manage existing web assets effectively.
Domain Names and Comparison
When comparing different aspects of various domain name options, factors such as cost, brand relevance, and availability need careful consideration. For instance, choosing between a generic top-level domain (gTLD) like .com or country code top-level domain (ccTLD) like .uk involves evaluating their suitability for your website’s purpose and target audience.
Making an informed decision about which domain name best suits your needs requires thorough comparison based on these factors.
Moreover, understanding how different domains function within specific industry niches can help in making strategic decisions when selecting an appropriate domain for your business or personal use.
Registering whats is domain name?
Involved Process
Registering a domain name involves choosing a unique web address for your website. The process starts with selecting an available domain name that reflects your brand or business. Once chosen, the next step is to check its name availability and register it through a domain registrar.
After registration, the domain needs to be linked to an IP address through DNS resolution, allowing internet users to access the website by typing in the domain name.
Understanding the registration and activation process for a new domain name is crucial. This typically involves providing accurate contact information and choosing the desired registration period for the domain name, often ranging from one to ten years. Activation usually occurs shortly after successful registration, making the domain name accessible on the internet.
Cost of Aquiring
Factors influencing the cost of acquiring and maintaining whats is domain name include its extension (.com, .net, .org), registrar fees, and any additional services like privacy protection or email hosting.
Different pricing models exist for purchasing and renewing domains; some registrars offer discounted rates for first-time registrations but regular prices upon renewal.
Understanding these financial aspects associated with owning a domain name can help individuals or businesses budget effectively while ensuring continuous ownership of their chosen web address.
Managing Domain Name Security
There are common security concerns, such as whats is domain name, that need to be addressed. One of the main issues is the vulnerability of DNS records and domain name, making them susceptible to unauthorized alterations or attacks. By implementing DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), domain owners can add an extra layer of protection against these types of threats.
Regularly updating and monitoring DNS records for the domain name is crucial for improved security. This involves keeping track of changes made to the DNS database and ensuring that they align with the authorized domain name configurations. Any discrepancies could indicate potential security breaches, making regular monitoring essential in maintaining a secure domain name system.
Utilizing general purpose security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access control lists can also safeguard domain name assets from various forms of cyber threats. These measures help protect the name associated with the domain, ensuring that unauthorized parties are unable to compromise its integrity.
Importance of Choosing the Right Domain Name
There are several benefits that can positively impact your business. A well-chosen web address (whats is domain name) can significantly enhance brand recognition, customer trust, and online visibility. By selecting a domain name that reflects your brand or business purpose, you make it easier for users to remember and access your website.
Tips on selecting a perfect domain include choosing a name that aligns with your brand identity and is easy to recall. Incorporating relevant keywords into your domain name can boost its performance in search engine results. It’s also essential to keep track of DNS resolution and domain name zones to ensure smooth internet resource access.
For businesses, the process of setting up a new or existing website effectively using the chosen web address and domain name involves configuring DNS settings, email hosting, SSL certificates, among other best practices for optimal website performance. Moreover, ensuring seamless integration between the selected domain name and your online presence is crucial for maximizing its impact.
Transferring and Ownership of Domain Names
Transferring Process
When transferring a domain name, it’s essential to provide accurate and updated information during the registration process. This includes details such as whats is domain name of registrant, address, email, contact number, and domain. These details, including domain name, are crucial for maintaining ownership and facilitating transfers if necessary.
Legal implications also come into play when updating ownership details for web addresses and domain names. It’s important to ensure that all information provided complies with legal requirements to avoid any potential disputes or issues in the future.
Responsibility
Owning a web address comes with responsibilities such as ensuring that the domain name is used ethically and in compliance with relevant policies. There are compliance requirements associated with managing or operating under your chosen domain name that must be adhered to at all times.
Ownership Details
The management of global web addresses falls under the purview of various organizations responsible for overseeing domain names on the internet. These governing bodies regulate policies, standards, and practices related to web addresses to ensure stability, security, and fairness across all domains.
Collaborative efforts among these managing bodies aim to maintain an equitable environment for all users of internet resources by upholding ethical use practices while exercising ownership rights over their respective domain names.
Who Manages Domain Names?
Responsibility
Domain name owners are responsible for maintaining accurate and up-to-date contact information in the WHOIS database. This ensures that they can be reached if any issues arise regarding their domain names.
It is crucial for domain name registrars to fulfill their responsibility of tracking and managing the domain names they sell. By doing so, they contribute to ensuring proper DNS resolution. Allowing internet users to access domain name websites without any disruptions.
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers. (ICANN) plays a pivotal role in overseeing the general purpose of domain names. As such, ICANN manages the global DNS database and protocol, which are essential components. In facilitating seamless internet resource access, including domain name.
Managing Bodies
Various bodies oversee the allocation of domain names within specific zones, contributing to the efficient functioning of the internet’s infrastructure. These entities play a vital role in tracking and managing the general purpose of domain names. Thereby, ensuring that each domain operates effectively within its designated zone.
In essence, these managing bodies are instrumental in supervising critical components such as DNS resolution. Moreover, The DNS database, and domain name, ultimately contributing to an optimized online experience for users worldwide.
In Summary
Understanding the structure, registration process. Security management, and the significance of choosing the right domain name are crucial aspects of managing a domain. The differences between domain names and URLs, as well as the transfer and ownership processes. Furthermore, contribute to a comprehensive understanding of domain name management.
Who manages domain names, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their online presence and security.
Furthermore, insights into maximizing the potential of domain names and ensuring their effective management. Readers are encouraged to explore additional resources from reputable sources in the field.
GET IN TOUCH
Transform your online presence with 360 E Market’s Web Development services! Elevate your website’s functionality and design for a seamless user experience. Explore our Web Development solutions to enhance your digital footprint!
Frequently Asked Questions
Whats is domain name?
A domain name is the address of a website that people type in the browser’s URL bar. To visit a specific website. It serves as an easy-to-remember alias for the numeric IP address of a web server. (whats is domain name)
whats is domain name structured?
Domain names are organized from right to left. With the top-level domain (TLD) at the far right and then moving leftward through second-level domains and subdomains.
What is the difference between a domain name and URL?
A domain name refers to the website’s address, while a URL (Uniform Resource Locator). Specific page addresses within that site.
How can one register a domain name?
One needs to choose an accredited registrar, verify if their desired domain is available. Pay registration fees, and agree to terms and conditions.
Why is choosing the right domain name important?
Selecting an appropriate domain name impacts brand identity, SEO performance, credibility, memorability, and user experience. It plays a crucial role in shaping online success.